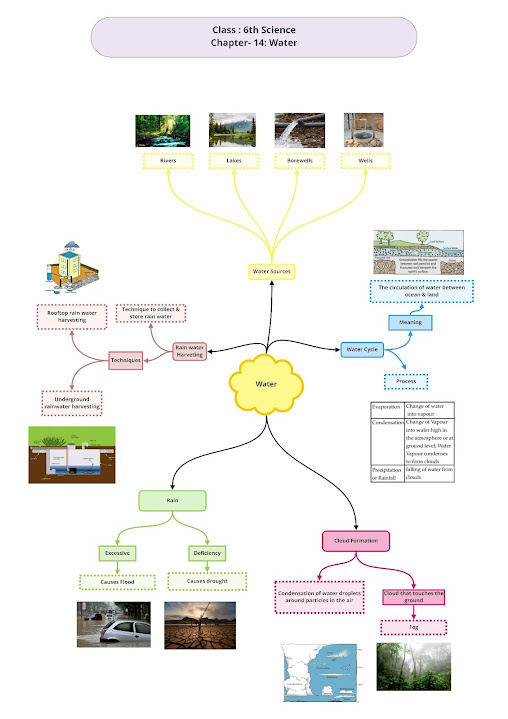
Water
Introduction
• Water is one of the most important natural resources.
• It is one of the basic necessities for survival.
Uses of Water
States of Water
• In nature, water is the only substance which exists in all the three states- solid, liquid and gas
Processes Involved in the Water Cycle
• During the water cycle in nature, the water goes through changes of state.
• Many physical processes such as evaporation, transpiration, condensation, freezing and melting are involved in the water cycle.
Importance of Water Cycle
• It makes fresh water available in the form of rain.
• It keeps the amount of water on the Earth’s surface constant.
Rains
Importance of Rain
• Rains bring relief by cooling the environment after the hot summer season.
• The sowing of many crops depends on the arrival of rain during monsoon.
• Rains provide water to the rivers and dams of hydroelectric power plants.
• Rains fill up lakes and ponds which act as sources of water.
• Rains get accumulated in the form of groundwater which gets stored under the surface of the Earth.
Adverse Effects of Rain
Conservation of Water
• Water is a very precious resource. Life on Earth will continue only as long as we have enough clean water.
• We should try to save water by controlling the amount of water which we use.
• We should be careful and use only as much water as required.
Harvesting
Rainwater which falls on roofs and terraces of buildings can be collected through pipes and stored in underground tanks or can be allowed to percolate into the soil and used to recharge the groundwater table. This is called water harvesting or rainwater harvesting.
Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1. Which one is a process in which water changes into vapours in atmosphere?
(a) Evaporation
(b) transpiration
(c) Precipitation
(d) condensation
Question 2. Potable water is
(a) ocean water
(b) groundwater at selected places
(c) river water
(d) ponds water
Question 3. Which is not a part of water cycle?
(a) Cloud formation
(b) Rain
(c) Drinking by animals
(d) Sun
Question 4. Which is a result of condensation of water vapours?
(a) Rain
(b) Snowfall
(c) Hail
(d) Tiny water droplets
Question 5. Which one is the purest form of water?
(a) River water
(b) Groundwater
(c) Rainwater
(d) Ocean water
Question 6. Circulation of water between ocean and land is known as
(a) water cycle
(b) rain cycle
(c) water management
(d) water harvesting
Question 7. The percentage of water in potato is
(a) 88
(b) 75
(c) 90
(d) 95
Question 8. Out of these, which is not a source of surface water?
(a) rain water
(b) river and lake water
(c) Spring water
(d) sea water
Question 9. Boiling point of water is
(a) 100°C
(c) 101°C
(b) 99°C
(d) 102°C
Question 10. Plants release large amount of water vapour into the atmosphere by the process called
(a) evaporation
(b) condensation
(c) precipitation
(d) transpiration
Very Short Question:
1. Write the sources of water on the earth.
2. In which forms, water exists on the earth?
3. What is transpiration?
4. How are the clouds formed?
5. What is meant by the conservation of water?
Short Questions:
1. Mention two main functions of water for living organisms.
2. Why is ocean water not suitable for domestic use?
3. Why does the water split on the floor disappear after some time?
4. How does heavy rain affect us?
5. How does the failure of rainfall affect people on the earth?
6. Name two processes responsible for the formation of clouds.
There are 4 containers A, B, C and D with same amount of water in each. Answer the following based on them.
(a) Name the container in which water will evaporate faster than all others.
(b) Name the container in which water will evaporate very slowly.
Give reason for your answer.
8. During winters why do we see more fog in close areas where there are lots of .trees?
Long Questions:
1. What is meant by conservation of water? Suggest three methods to conserve water.
2. What is rainwater harvesting? Describe the method of rainwater harvesting.
3. The process of condensation plays an important role in bringing water back to the surface of earth. Explain how?
Answer Key-
Multiple Choice Answers:
1. (a) Evaporation
2. (b) groundwater at selected places
3. (c) Drinking by animals
4. (d) Tiny water droplets
5. (c) Rainwater
6. (a) water cycle
7. (b) 75
8. (c) Spring water
9. (a) 100°C
10. (d) transpiration
Very Short Answers:
1. Answer: Sources of water on the earth are:
Seas, Oceans, Rivers, Springs, Tubewells, etc.
2. Answer: Water exists on the earth in all three physical forms: ice, water and water vapour.
3. Answer: Loss of water in the form of water vapour through stomata of leaves is called transpiration.
4. Answer: Clouds are formed by the condensation of water vapour at high altitude.
5. Answer: Careful, economical and wise use of water and avoiding the wastage of water is called conservation of water.
Short Answer:
1. Answer: Two main functions of water for living organisms are:
1. Water is essential for the germination of seeds, growth of plants and in photosynthesis.
2. Water is used for the transportation of people and goods.
2. Answer: Sea and ocean water contains large amounts of various salts. It is due to these salts the ocean water is salty and cannot be used for drinking, washing and for irrigation purposes.
3. Answer: Due to evaporation the water split is changed into water vapour. So it disappears after some time.
4. Answer: Heavy rains may cause:
1. A rise of water level in dams, rivers, lakes, etc.
2. Waterlogging and floods.
3. Floods cause damage to property, crops and animals.
5. Answer: The failure of rainfall can cause the following:
1.The soil becomes dry.
2. Water level in rivers, lakes, dams, etc. may fall. Ponds and canals may even dry up.
3. The ground water level falls.
6. Answer: Evaporation and transpiration.
7. Answer:
(a) C - More is the exposed surface area, more will be evaporation of water.
(b) B - As it is closed, no evaporation takes place.
8. Answer: Due to lots of trees, air at that place contains much more water vapour during winters. These vapours condense on dust or smoke particles forming thick fog.
Long Answer:
1. Answer: Careful and economical use of water and avoiding its wastage is called conservation of water.
Suggestions for conserving water:
i. Use only the required quantity of water.
ii. Trees and forests help in causing rainfall. So, to conserve water, we should plant more and more trees.
iii. By collecting rainwater in tanks, ponds or by constructing check dams.
2. Answer: Rainwater harvesting is the collection of rainwater and storing for future use. In this system rainwater in collected from the rooftops by means of pipes into storage tank for later use.
Methods of Rainwater Harvesting:
i. Rooftop rainwater harvesting. In this system, the rainwater from the rooftop is collected in a storage tank, through pipes.
ii. Another method, a big pit is dug near house for collecting rainwater. This pit is filled with different layers of bricks, coarse gravels and sand or granite pieces.
3. Answer: The Water Cycle is the journey of water from the land to the sky and back again. There are six important processes that make up the water cycle.
Condensation – the opposite of evaporation. Condensation occurs when a gas is changed into a liquid.
Infiltration – Infiltration is an important process where rain water soaks into the ground, through the soil and underlying rock layers.
Runoff – Much of the water that returns to Earth as precipitation runs off the surface of the land, and flows down hill into streams, rivers, ponds and lakes.
Evaporation – the process where a liquid, in this case water, changes from its liquid state to a gaseous state.
Precipitation – When the temperature and atmospheric pressure are right, the small droplets of water in clouds form larger droplets and precipitation occurs. The raindrops fall to Earth.
Transpiration – As plants absorb water from the soil, the water moves from the roots through the stems to the leaves. Once the water reaches the leaves, some of it evaporates from the leaves, adding to the amount of water vapour in the air. This process of evaporation through plant leaves is called transpiration.

























0 Comments