Class 8 Science Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a ___________
(b) Blue green algae fix _________ directly from air to enhance fertility of soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of a microorganism ___________
(d) Cholera is caused by __________
Answer:
(a) Microscope
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Yeast
(d) Bacteria
(a) Microorganisms can be seen with the help of a ___________
(b) Blue green algae fix _________ directly from air to enhance fertility of soil.
(c) Alcohol is produced with the help of a microorganism ___________
(d) Cholera is caused by __________
Answer:
(a) Microscope
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Yeast
(d) Bacteria
2. Tick the correct answer:
(a) Yeast is used in the production of
(i) sugar
(ii) alcohol
(iii) hydrochloric acid
(iv) oxygen
Answer:
(ii) Alcohol
(a) Yeast is used in the production of
(i) sugar
(ii) alcohol
(iii) hydrochloric acid
(iv) oxygen
Answer:
(ii) Alcohol
(b) Which one of the following is an antibiotic?
(i) Sodium bicarbonate
(ii) Streptomycin
(iii) Alcohol
(iv) Yeast
Answer:
(ii) Streptomycin
(c) Carrier of malaria-causing protozoan is
(i) female Anopheles mosquito
(ii) cockroach
(iii) housefly
(iv) butterfly
Answer:
(i) Female Anopheles Mosquito
(d) The most common carrier of communicable diseases is
(i) ant
(ii) housefly
(iii) dragonfly
(iv) spider
Answer:
(ii) Housefly
(e) The bread or idli dough rises because of
(i) heat
(ii) grinding
(iii) growth of yeast cells
(iv) kneading
Answer:
(iii) growth of yeast cells
(f) The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol is called
(i) nitrogen inflation
(ii) moulding
(iii) fermentation
(iv) infection
Answer:
(iii) fermentation
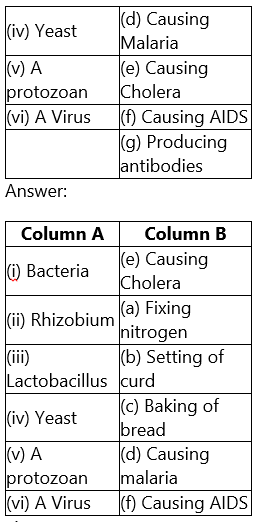
3. Match the organisms in Column A with their action in Column B.
4. Can microorganisms be seen with the naked eye? If not, how can they be seen?
Answer: No, we cannot see microorganisms with the naked eye. They can be seen with the help of a microscope.
Answer: No, we cannot see microorganisms with the naked eye. They can be seen with the help of a microscope.
5. What are the major groups of microorganisms?
Answer: The major groups of microorganisms are bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa.
Answer: The major groups of microorganisms are bacteria, fungi, algae, and protozoa.
6. Name the microorganisms which can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Answer: Bacteria e.g., Rhizobium, Azotobactor, and blue-green algae e.g., Anabaena and Nostoc can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
Answer: Bacteria e.g., Rhizobium, Azotobactor, and blue-green algae e.g., Anabaena and Nostoc can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.
7. Write 10 lines on the usefulness of microorganisms in our lives.
Answer: The uses of microorganisms are:
1. Microorganisms are utilized in the preparation of wines, pickles, vinegar, cheese, curds, the aroma in tobacco.
2. They are used in the production of antibiotics.
3. They help in sewage disposal.
4. Some soil bacteria like Rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen, which is useful for plants.
5. Some microorganisms are used for the large-scale production of alcohol, wine, and acetic acid.
6. Milk is turned into curd by bacteria.
7. Some bacteria help in tanning leather.
8. Some microorganisms are used to produce vaccines.
9. They clean the environment.
10. Some bacteria tenderize meat by breaking down muscle fibers.
Answer: The uses of microorganisms are:
1. Microorganisms are utilized in the preparation of wines, pickles, vinegar, cheese, curds, the aroma in tobacco.
2. They are used in the production of antibiotics.
3. They help in sewage disposal.
4. Some soil bacteria like Rhizobium fix atmospheric nitrogen, which is useful for plants.
5. Some microorganisms are used for the large-scale production of alcohol, wine, and acetic acid.
6. Milk is turned into curd by bacteria.
7. Some bacteria help in tanning leather.
8. Some microorganisms are used to produce vaccines.
9. They clean the environment.
10. Some bacteria tenderize meat by breaking down muscle fibers.
8. Write a short paragraph on the harms caused by microorganisms.
Answer: The harms caused by microorganisms are:
• They cause a number of diseases in men, plants, and animals.
• Some microorganisms spoil milk, pickles, jams, squashes, and other food items.
• They damage the crops and thus, reducing productivity.
Answer: The harms caused by microorganisms are:
• They cause a number of diseases in men, plants, and animals.
• Some microorganisms spoil milk, pickles, jams, squashes, and other food items.
• They damage the crops and thus, reducing productivity.
9. What are antibiotics? What precautions must be taken while taking antibiotics?
Answer: Antibiotics are medicines that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. Antibiotics must be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor. The course of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor must be finished. Antibiotics must not be taken when not needed, because this helps bacteria in our body to develop resistance to them. Next time when we fall ill and need these antibiotics then there would be less effectiveness.
Answer: Antibiotics are medicines that kill or stop the growth of disease-causing microorganisms. Antibiotics must be taken only on the advice of a qualified doctor. The course of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor must be finished. Antibiotics must not be taken when not needed, because this helps bacteria in our body to develop resistance to them. Next time when we fall ill and need these antibiotics then there would be less effectiveness.
1. What are microorganisms?
Answer: Microorganisms are living organisms which cannot be seen with unaided eyes, they can be seen only through the powerful microscope.
Answer: Microorganisms are living organisms which cannot be seen with unaided eyes, they can be seen only through the powerful microscope.
2. What happens to moist bread during the rainy season?
Answer: During the rainy season, moist bread gets spoilt and its surface gets covered with greyish white patches.
Answer: During the rainy season, moist bread gets spoilt and its surface gets covered with greyish white patches.
3. What are viruses?
Answer: Viruses are disease-causing agents and are very minute particles visible only under an electron microscope. They are smaller than bacteria.
Answer: Viruses are disease-causing agents and are very minute particles visible only under an electron microscope. They are smaller than bacteria.
4. Name few diseases caused by virsues.
Answer: Rabies, polio, chickenpox, common cold, influenza (flu), and mosaic of tobacco and potato are the diseases caused by viruses.
Answer: Rabies, polio, chickenpox, common cold, influenza (flu), and mosaic of tobacco and potato are the diseases caused by viruses.
5. Where do microorganisms live?
Answer: Microorganisms live in the soil, mud, water, sea, air, plants, animals, food products, various utensils, etc, and on dead weeds, leaves, clothes, books, jams, pickles, dung, shoes, etc. They also live in man and animals. Amoeba lives alone. Fungi and bacteria live in colonies.
Answer: Microorganisms live in the soil, mud, water, sea, air, plants, animals, food products, various utensils, etc, and on dead weeds, leaves, clothes, books, jams, pickles, dung, shoes, etc. They also live in man and animals. Amoeba lives alone. Fungi and bacteria live in colonies.
6. State some beneficial effects of bacteria.
Answer: The beneficial effects of bacteria are:
1. They bring about the decomposition of wastes in the soil and thus, increase the fertility of the soil.
2. Some of the putrifying bacteria decompose the matter of sewage and help in sewage disposal.
3. Some bacteria help in tanning leather.
4. Bacteria tenderize meat by breaking down muscle fibers.
5. Curd, cheese, etc. are formed by the action of bacteria in the milk.
6. The fermentation activity of bacteria is useful in the preparation of vinegar, wine, palm juice, etc.
7. Filamentous bacteria are used in the production of antibiotics.
8. Some bacteria like Rhizobium can fix the nitrogen of the atmosphere, thus, enriching the soil in the nitrogen contents.
Answer: The beneficial effects of bacteria are:
1. They bring about the decomposition of wastes in the soil and thus, increase the fertility of the soil.
2. Some of the putrifying bacteria decompose the matter of sewage and help in sewage disposal.
3. Some bacteria help in tanning leather.
4. Bacteria tenderize meat by breaking down muscle fibers.
5. Curd, cheese, etc. are formed by the action of bacteria in the milk.
6. The fermentation activity of bacteria is useful in the preparation of vinegar, wine, palm juice, etc.
7. Filamentous bacteria are used in the production of antibiotics.
8. Some bacteria like Rhizobium can fix the nitrogen of the atmosphere, thus, enriching the soil in the nitrogen contents.
7. Name the bacteria that convert milk into curd.
Answer: Lactobacillus.
Answer: Lactobacillus.
8. Name the bacteria used for the production of acetic acid from alcohol.
Answer: Acetobacter acetic.
Answer: Acetobacter acetic.
9. What are yeasts? What is their shape? How do they reproduce?
Answer: Yeasts are (saccharomyces) unicellular and saprophytic fungi. The shape of yeast cells is spherical, elliptical, or cylindrical. Yeast reproduces through asexual mode by budding or by binary fission.
Answer: Yeasts are (saccharomyces) unicellular and saprophytic fungi. The shape of yeast cells is spherical, elliptical, or cylindrical. Yeast reproduces through asexual mode by budding or by binary fission.
10. Name the gas produced by yeast during respiration.
Answer: Carbon dioxide.
Answer: Carbon dioxide.
11.
1. Name the common antibiotic.
2. Name the antibiotics made from bacteria and fungi.
Answer:
1. Penicillin
2. Streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin.
1. Name the common antibiotic.
2. Name the antibiotics made from bacteria and fungi.
Answer:
1. Penicillin
2. Streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin.
12. Who discovered penicillin?
Answer: Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1929.
Answer: Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin in 1929.
13. Draw a diagram to show blue-green algae.
Answer:
Answer:
14. Describe the role of blue-green algae in the fertility of the soil.
Answer: Blue-green algae have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds. It increases the humus content of the soil. This improves the water-holding capacity of the soil. Due to these reasons, the fertility of the soil is increased and hence, crop growth is also increased.
Answer: Blue-green algae have the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds. It increases the humus content of the soil. This improves the water-holding capacity of the soil. Due to these reasons, the fertility of the soil is increased and hence, crop growth is also increased.
15. What are pathogens?
Answer: Microorganisms causing diseases in human beings, plants, and animals are called pathogens.
Answer: Microorganisms causing diseases in human beings, plants, and animals are called pathogens.
16. How do disease-causing microorganisms enter our bodies?
Answer: Disease-causing microorganisms enter our body through the air we breathe, the water we drink, or the food we eat; or transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or through an animal carrier.
Answer: Disease-causing microorganisms enter our body through the air we breathe, the water we drink, or the food we eat; or transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or through an animal carrier.
17. What are communicable diseases?
Answer: Communicable diseases are those microbial diseases which are spread from an infected person to a healthy person through the air, water, food, or physical contact e.g., malaria, T.B, AIDS, cholera, common cold, chickenpox, etc.
Answer: Communicable diseases are those microbial diseases which are spread from an infected person to a healthy person through the air, water, food, or physical contact e.g., malaria, T.B, AIDS, cholera, common cold, chickenpox, etc.
18. How is the plasmodium parasite causing malaria transmission?
Answer: Plasmodium parasite is transmitted by the bite of the female anopheles mosquito. Anopheles mosquito merely acts as a carrier of malaria-causing parasites. It takes them alongwith the blood sucked from an infected person and transmits them to a healthy person.
Answer: Plasmodium parasite is transmitted by the bite of the female anopheles mosquito. Anopheles mosquito merely acts as a carrier of malaria-causing parasites. It takes them alongwith the blood sucked from an infected person and transmits them to a healthy person.
19. What is a causative microorganism of chickenpox and polio?
Answer: Disease – Causative microorganism
Chicken Pox – Virus
Polio – Virus
20. What is a mode of transmission of causative microorganisms chickenpox and polio?
Answer: Chicken Pox – Air, contact
Polio – Air, water.
Answer: Chicken Pox – Air, contact
Polio – Air, water.
21. What is a causative microorganism of cholera and typhoid?
Answer: Bacteria.
Answer: Bacteria.
22. What is anthrax?
Answer: Anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium.
Answer: Anthrax is a dangerous human and cattle disease caused by a bacterium.
23. Name a disease of cattle caused by a virus.
Answer: Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
Answer: Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
24. Name the bacteria which causes anthrax disease.
Answer: Bacillus anthracis.
Answer: Bacillus anthracis.
25. Who discovered the bacterium which causes anthrax disease?
Answer: Robert Koch (1876).
Answer: Robert Koch (1876).
26. Name a disease in plants caused by bacteria. What is its mode of transmission?
Answer: Citrus canker. Its mode of transmission is air.
Answer: Citrus canker. Its mode of transmission is air.
27. Name a disease in plants caused by fungi. What is its mode of transmission?
Answer: Rust of wheat. Its mode of transmission is insects and seeds.
Answer: Rust of wheat. Its mode of transmission is insects and seeds.
28. Name a disease in plants caused by viruses. What is its mode of transmission?
Answer: Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi. Its mode of transmission is insect.
Answer: Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi. Its mode of transmission is insect.
29. How food can become a ‘poison’?
Answer: Microorganisms that grow on our food sometimes produce toxic substances. These make the food poisonous causing serious illness and even death.
Answer: Microorganisms that grow on our food sometimes produce toxic substances. These make the food poisonous causing serious illness and even death.
30. What is food poisoning?
Answer: Food poisoning is due to the consumption of food spoilt by some microorganisms.
Answer: Food poisoning is due to the consumption of food spoilt by some microorganisms.
31. Is spoiling food a chemical reaction?
Answer: Yes.
Answer: Yes.
32. What happens when food gets spoiled?
Answer: Spoiled food emits a bad smell and has a bad taste and changed colour.
Answer: Spoiled food emits a bad smell and has a bad taste and changed colour.
33. What is the role of nodules in the biological fixation of nitrogen?
Answer: The role of nodules in the biological fixation of nitrogen is to fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates.
Answer: The role of nodules in the biological fixation of nitrogen is to fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrates.
34. Name the bacteria which can fix nitrogen present in the air.
Answer: Rhizobium, Clostridium, and Azotobacter.
Answer: Rhizobium, Clostridium, and Azotobacter.
35. Name the most abundant gas present in the air. What is its percentage in our atmosphere?
Answer: Nitrogen. Our atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen gas.
Answer: Nitrogen. Our atmosphere consists of 78% nitrogen gas.
36. In which form is nitrogen present in all living organisms?
Answer: Proteins, chlorophyll, nucleic acids, and vitamins.
Answer: Proteins, chlorophyll, nucleic acids, and vitamins.
37. With the help of a labelled diagram explain the various stages of the nitrogen cycle.
Answer: The various stages of the nitrogen cycle are:
1. In the soil nitrogen is present in the form of nitrates by the following processes:
o Nitrogen and oxygen combine to form nitric acid at the time of lightning in the atmosphere. This nitric acid forms nitrates which reach the earth with rainwater.
o Nitrates are formed in the soil from the decay of dead plants and animals.
o Nitrogen-fixing bacteria present in soil and root nodules of some leguminous plants convert the nitrogen in the air directly into nitrates.
2. The plants absorb nitrates from the soil and convert them into plant proteins and plant protoplasm.
3. The animals eat plants and convert plant proteins into animal proteins.
4. The plant proteins and animal proteins of dead plants and animals are converted into ammonia in the soil by bacterial decomposition.
5. Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and these nitrates are converted into nitrates in the soil.
6. Some of the nitrates formed in the soil are converted back into free nitrogen gas by
denitrifying bacteria. This free nitrogen gas goes back into the atmosphere and the nitrogen cycle is repeated again and again.
Answer: The various stages of the nitrogen cycle are:
1. In the soil nitrogen is present in the form of nitrates by the following processes:
o Nitrogen and oxygen combine to form nitric acid at the time of lightning in the atmosphere. This nitric acid forms nitrates which reach the earth with rainwater.
o Nitrates are formed in the soil from the decay of dead plants and animals.
o Nitrogen-fixing bacteria present in soil and root nodules of some leguminous plants convert the nitrogen in the air directly into nitrates.
2. The plants absorb nitrates from the soil and convert them into plant proteins and plant protoplasm.
3. The animals eat plants and convert plant proteins into animal proteins.
4. The plant proteins and animal proteins of dead plants and animals are converted into ammonia in the soil by bacterial decomposition.
5. Nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and these nitrates are converted into nitrates in the soil.
6. Some of the nitrates formed in the soil are converted back into free nitrogen gas by
denitrifying bacteria. This free nitrogen gas goes back into the atmosphere and the nitrogen cycle is repeated again and again.

















0 Comments