Chapter 11 Cell Structure and Functions
1. Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
1. Unicellular organisms have one-celled bodies.
2. Muscle cells are branched.
3. The basic living unit of an organism is an organ.
4. Amoeba has an irregular shape.
Answer:
1. True
2. False
3. False
4. True
1. Unicellular organisms have one-celled bodies.
2. Muscle cells are branched.
3. The basic living unit of an organism is an organ.
4. Amoeba has an irregular shape.
Answer:
1. True
2. False
3. False
4. True
2. Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
Answer:
The nerve cell receives and transfers messages, thereby helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body.
Answer:
The nerve cell receives and transfers messages, thereby helping to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body.
3. Write short notes on the following:
(i) Cytoplasm
(ii) Nucleus of a cell
Answer:
(i) Cytoplasm. It is the fluid present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various components or organelles of cells, e.g., mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc. are present in it. The cytoplasm is made up of basic elements like C, H, O, N. They are found in the form of chemical substances like carbohydrates, proteins, and water. These substances are present in all the cells of every organism.
(ii) Nucleus of a cell. The nucleus is a cell organelle in the middle of a cell. It is dense and round. In the plant cells, the nucleus lies in the periphery of the cell. The nucleus has a liquid protoplasm called nucleoplasm. It is bounded by a nuclear membrane. The nucleus controls the activities of the cells. It contains a network of fibrous material called chromatin. The condensed chromatin is in the form of fiber structures called chromosomes, which help in the inheritance or transfer of characters from parents to the next generation.
(i) Cytoplasm
(ii) Nucleus of a cell
Answer:
(i) Cytoplasm. It is the fluid present between the cell membrane and the nucleus. Various components or organelles of cells, e.g., mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes, etc. are present in it. The cytoplasm is made up of basic elements like C, H, O, N. They are found in the form of chemical substances like carbohydrates, proteins, and water. These substances are present in all the cells of every organism.
(ii) Nucleus of a cell. The nucleus is a cell organelle in the middle of a cell. It is dense and round. In the plant cells, the nucleus lies in the periphery of the cell. The nucleus has a liquid protoplasm called nucleoplasm. It is bounded by a nuclear membrane. The nucleus controls the activities of the cells. It contains a network of fibrous material called chromatin. The condensed chromatin is in the form of fiber structures called chromosomes, which help in the inheritance or transfer of characters from parents to the next generation.
4. Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Answer: Cytoplasm.
Answer: Cytoplasm.
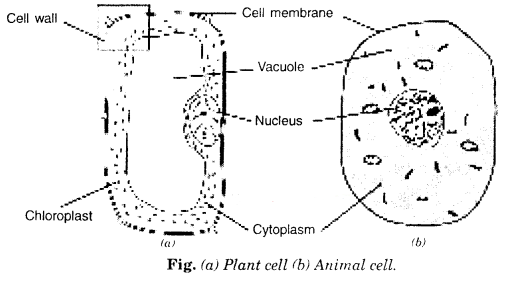
5. Makes sketches of animal and plant cells state three differences between them.
Answer: Differences between plant cell and animal cells are
Answer: Differences between plant cell and animal cells are
6. State a difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Answer: Differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes are:
7. Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their function.
Answer: Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell. They carry genes and help in inheritance i.e., transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
Answer: Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the cell. They carry genes and help in inheritance i.e., transfer of characters from the parents to the offspring.
8. “Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms.” Explain.
Answer: As building cannot be built without bricks, in the same way living organisms can not be formed without cells. The buildings are built of similar bricks having different designs, shapes, and sizes. Similarly in the living world, organisms differ from one another but all are made up of cells. Thus it is said that cells are the basic structural units of living organisms.
Answer: As building cannot be built without bricks, in the same way living organisms can not be formed without cells. The buildings are built of similar bricks having different designs, shapes, and sizes. Similarly in the living world, organisms differ from one another but all are made up of cells. Thus it is said that cells are the basic structural units of living organisms.
9. Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
Answer: Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which synthesizes food in plants by the process of photosynthesis. No photosynthesis occurs in animals. So, they do not contain chloroplasts.
Answer: Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which synthesizes food in plants by the process of photosynthesis. No photosynthesis occurs in animals. So, they do not contain chloroplasts.
10. Complete the following cross-word with the help of clues given.
Across
1. This is necessary for photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the coil.
8. Units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down
1. Green plastids.
2. Formed by a collection of tissues.
4. It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding medium.
5. Empty space in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells.
Answer:
Across
1. This is necessary for photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the coil.
8. Units of inheritance present on the chromosomes.
Down
1. Green plastids.
2. Formed by a collection of tissues.
4. It separates the contents of the cell from the surrounding medium.
5. Empty space in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells.
Answer:
Cell Structure and Functions Additional s and Answers
1. Name the basic structural units of living organisms.
Answer: Cells.
Answer: Cells.
2. Who coined the word cell?
Answer: Robert Hooke coined the word cell in the 17th century while observing the cook slice under the microscope.
Answer: Robert Hooke coined the word cell in the 17th century while observing the cook slice under the microscope.
3. What are cells?
Answer: Cells are basic structural units of living organisms.
Answer: Cells are basic structural units of living organisms.
4. What are unicellular organisms? Give examples.
Answer: Single-celled organisms are called unicellular organisms. All the functions of unicellular organisms are carried out in the same cell. Examples are Amoeba, Paramecium.
Answer: Single-celled organisms are called unicellular organisms. All the functions of unicellular organisms are carried out in the same cell. Examples are Amoeba, Paramecium.
5. What are multicellular organisms?
Answer: Organisms which have a large number of cells are called multicellular organisms. A multicellular has millions of cells. There are specialized cells for different functions of multicellular organisms.
Answer: Organisms which have a large number of cells are called multicellular organisms. A multicellular has millions of cells. There are specialized cells for different functions of multicellular organisms.
6. What is a tissue?
Answer: A tissue is a group of similar cells performing a specific function.
Answer: A tissue is a group of similar cells performing a specific function.
7. What are the basic components of a cell?
Answer: The basic components of a cell are the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
Answer: The basic components of a cell are the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
8. What is a cell organelle?
Answer: Cells organelles are smaller components or parts of the cell present inside it.
Answer: Cells organelles are smaller components or parts of the cell present inside it.
9. Name the membrane which bounds the cells.
Answer: Plasma membrane or cell membrane.
Answer: Plasma membrane or cell membrane.
10. Name the liquid substance present in the cell.
Answer: Protoplasm.
Answer: Protoplasm.


















0 Comments