The Four Vedas
The period in which the Vedas were composed in the Indian subcontinent is known as the Vedic Age. The Vedas were composed by the Aryans. There are four Vedas- the Rigveda, the Samaveda, the Yajurveda and the Arthaveda.
The period in which the Vedas were composed in the Indian subcontinent is known as the Vedic Age. The Vedas were composed by the Aryans. There are four Vedas- the Rigveda, the Samaveda, the Yajurveda and the Arthaveda.
Rigveda
Following are some facts about the Rigveda:
• Rigveda is the oldest written Veda which was composed about 3,500 years ago in old sanskrita.
• It includes more than a thousand hymns called sukta. These hymns have been written in praise of various gods and goddesses such as Agni (the fire god) and Indra (the warrior god).
• These hymns were written by the sages. Knowledge
in the Vedas was imparted by the priests to the students with great care. The Rigveda was mostly heard and recited rather than read.
• Most of these hymns were composed by men and only a few were composed by women.
• Historians learnt about the Vedic Age not only through archaeological sources but also through the interpretation of the Vedas.
• Many of the hymns in Rigveda are in the form of dialogues which has helped historians to reconstruct the Vedic history.
• There are a number of prayers in the Rigveda for cattle, children (especially sons) and horses.
Following are some facts about the Rigveda:
• Rigveda is the oldest written Veda which was composed about 3,500 years ago in old sanskrita.
• It includes more than a thousand hymns called sukta. These hymns have been written in praise of various gods and goddesses such as Agni (the fire god) and Indra (the warrior god).
• These hymns were written by the sages. Knowledge
in the Vedas was imparted by the priests to the students with great care. The Rigveda was mostly heard and recited rather than read.
• Most of these hymns were composed by men and only a few were composed by women.
• Historians learnt about the Vedic Age not only through archaeological sources but also through the interpretation of the Vedas.
• Many of the hymns in Rigveda are in the form of dialogues which has helped historians to reconstruct the Vedic history.
• There are a number of prayers in the Rigveda for cattle, children (especially sons) and horses.
How historians study the Rigveda
Some of the hymns in the Rigveda are in the form of dialogues. This is part of one such hymn, a dialogue between a sage named Vishvamitra, and two rivers, (Beas and Sutlej) that were worshipped as goddesses.
Some of the hymns in the Rigveda are in the form of dialogues. This is part of one such hymn, a dialogue between a sage named Vishvamitra, and two rivers, (Beas and Sutlej) that were worshipped as goddesses.
Cattle, horses and chariots
There are many prayers in the Rigveda for cattle, children (especially sons), and horses.
1. Horses were used in battles.
2. Battles were fought for land, water, and to capture people and cattle. There was no regular army, but there were assemblies where people met and discussed matters of war and peace. Most men took part in wars and also chose leaders.
3. Wealth was kept by the leaders, some were given to the priests and the rest was distributed amongst the people.
There are many prayers in the Rigveda for cattle, children (especially sons), and horses.
1. Horses were used in battles.
2. Battles were fought for land, water, and to capture people and cattle. There was no regular army, but there were assemblies where people met and discussed matters of war and peace. Most men took part in wars and also chose leaders.
3. Wealth was kept by the leaders, some were given to the priests and the rest was distributed amongst the people.
Words to describe people in Rigveda
Let us see some of the words used to describe people found in the Rigveda.
There are 2 groups who are described in terms of their work –
The priests: who were also called brahmins. They used to perform various rituals.
Let us see some of the words used to describe people found in the Rigveda.
There are 2 groups who are described in terms of their work –
The priests: who were also called brahmins. They used to perform various rituals.
The rajas: They did not have capital cities, palaces or armies, nor did they collect taxes. Sons did not automatically succeed fathers as rajas.
Two words were used to describe the people or the community as a whole:
1. One was jana
2. The other was vish
The people who composed the hymns described themselves as Aryas and called their opponents Dasas or Dasyus. The term dasa means slave. Slaves were women and men who were often captured in war.
Two words were used to describe the people or the community as a whole:
1. One was jana
2. The other was vish
The people who composed the hymns described themselves as Aryas and called their opponents Dasas or Dasyus. The term dasa means slave. Slaves were women and men who were often captured in war.
Sanskrit and Other Languages
Sanskrit is one of the Indo-European languages. Many Indian languages such as Gujarati, Assamese, Hindi and Kashmiri and foreign languages such as English, French, German and Greek belong to the family of Indo-European languages. These are called a family as originally they had many words in common.
Battles and Wars
• Horses and chariots are considered important in the Vedas as they were used in fighting wars and battles.
• Battles were fought for land, water and to capture people.
• Land was important as crops were grown on it.
• A major portion of the wealth which was obtained in battles was kept with the king. Some of the wealth was given to the priests and the rest was distributed amongst the people.
• Wealth was also used for the performing of the yajnas, in which sacrifices were made.There was no regular army and usually the men folk participated in the wars.
Sanskrit is one of the Indo-European languages. Many Indian languages such as Gujarati, Assamese, Hindi and Kashmiri and foreign languages such as English, French, German and Greek belong to the family of Indo-European languages. These are called a family as originally they had many words in common.
Battles and Wars
• Horses and chariots are considered important in the Vedas as they were used in fighting wars and battles.
• Battles were fought for land, water and to capture people.
• Land was important as crops were grown on it.
• A major portion of the wealth which was obtained in battles was kept with the king. Some of the wealth was given to the priests and the rest was distributed amongst the people.
• Wealth was also used for the performing of the yajnas, in which sacrifices were made.There was no regular army and usually the men folk participated in the wars.
People in the Vedic Age
• People were divided into various categories. The top position was occupied by the rajas and the priests (also known as Brahmins).
• The rajas in the early Vedic Period neither lived in palaces nor collected taxes. Their position was not hereditary.
• People who composed the Vedas were known as the Aryans and the slaves came to be known as the dasas or the dasyus. These were people who were captured in the wars.
• The dasas were not allowed to read and write and participate in the sacrifices.
• The word ‘jana’ referred to the community of people. Puru jana, Bharata jana and the Yadu jana were some communities of people at this time.
• People were divided into various categories. The top position was occupied by the rajas and the priests (also known as Brahmins).
• The rajas in the early Vedic Period neither lived in palaces nor collected taxes. Their position was not hereditary.
• People who composed the Vedas were known as the Aryans and the slaves came to be known as the dasas or the dasyus. These were people who were captured in the wars.
• The dasas were not allowed to read and write and participate in the sacrifices.
• The word ‘jana’ referred to the community of people. Puru jana, Bharata jana and the Yadu jana were some communities of people at this time.
Megaliths
The big boulders of stones which were arranged by the people of the Vedic Age to mark their burial sites are known as megaliths.
The big boulders of stones which were arranged by the people of the Vedic Age to mark their burial sites are known as megaliths.
Some important facts about megaliths are:
• The practice of erecting megaliths began about 3,000 years ago and this practice was prevalent in Deccan and North-East and Kashmir.
• Some megalithic sites were discovered at Adichanallur (present day Tamil Nadu) and Brahmagiri (present day Karnataka).
• While some megaliths were found on the surface of the earth, many were found underground.
• Generally, the dead were buried with pots which are now known as Black and Red Ware. Sometimes they were also buried with tools, horses and ornaments of stone and gold.
• At one burial site in Brahmagiri, one skeleton was found buried with 33 gold beads, 2 stone beads and 4 copper bangles. This shows that while some people were rich, some were poor.
• At many places, megaliths containing more than one person have been found. This shows that perhaps the members of the family were buried in the same place.
• In Inamgaon, at one burial site, adults were buried in the ground with their heads towards the north.
• One male skeleton was found to be buried in a large, four legged clay jar in the centre of a big five room house. This was one of the largest houses and also had a granary.
• Skeletons tell us about the buried person. About 2,000 years ago, a famous physician of India named ‘Charaka’ wrote a book on medicine known as Charaka Samhita. In his book, he concluded that the human body has 360 bones. He arrived at this figure by counting the teeth, joints and cartilage.
• The practice of erecting megaliths began about 3,000 years ago and this practice was prevalent in Deccan and North-East and Kashmir.
• Some megalithic sites were discovered at Adichanallur (present day Tamil Nadu) and Brahmagiri (present day Karnataka).
• While some megaliths were found on the surface of the earth, many were found underground.
• Generally, the dead were buried with pots which are now known as Black and Red Ware. Sometimes they were also buried with tools, horses and ornaments of stone and gold.
• At one burial site in Brahmagiri, one skeleton was found buried with 33 gold beads, 2 stone beads and 4 copper bangles. This shows that while some people were rich, some were poor.
• At many places, megaliths containing more than one person have been found. This shows that perhaps the members of the family were buried in the same place.
• In Inamgaon, at one burial site, adults were buried in the ground with their heads towards the north.
• One male skeleton was found to be buried in a large, four legged clay jar in the centre of a big five room house. This was one of the largest houses and also had a granary.
• Skeletons tell us about the buried person. About 2,000 years ago, a famous physician of India named ‘Charaka’ wrote a book on medicine known as Charaka Samhita. In his book, he concluded that the human body has 360 bones. He arrived at this figure by counting the teeth, joints and cartilage.
Occupations of the People of Inamgaon
Archaeologists in Inamgaon have found the seeds of crops such as wheat, rice, barley, millets and peas. This shows that people were engaged in agricultural activities. Remains of many animals such as cows, buffaloes, goats, sheep, asses, and blackbucks have been found. This exhibits that while many animals were herded, some were also used as food. There is also evidence that people collected and ate fruits such as amla, ber, jamun, dates and varieties of berries.
Thus, we find that various manuscripts, pottery, artifacts and burial practices give us a glimpse of how people lived in many hundred years ago.
Archaeologists in Inamgaon have found the seeds of crops such as wheat, rice, barley, millets and peas. This shows that people were engaged in agricultural activities. Remains of many animals such as cows, buffaloes, goats, sheep, asses, and blackbucks have been found. This exhibits that while many animals were herded, some were also used as food. There is also evidence that people collected and ate fruits such as amla, ber, jamun, dates and varieties of berries.
Thus, we find that various manuscripts, pottery, artifacts and burial practices give us a glimpse of how people lived in many hundred years ago.
Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1. Where was the head of the dead laid at the burials found at Inamgaon?
(a) East
(b) West
(c) North
(d) South
Question 2. Vessels found at Inamgaon site, contained:
(a) Food and water
(b) Ornaments
(c) Clothes
(d) None
Question 3. The language of the Veda is:
(a) Hindi
(b) Sanskrit
(c) Vedic Sanskrit
(d) Tamil
Question 4. Which of these does not comes under the Veda?
(a) Rig
(b) Atharva
(c) Sam
(d) Puran
Question 5. Inamgaon is situated on the river Ghod which is tributary of:
(a) Bhima
(b) Ravi
(c) Vias
(d) Ganga
Question 6. Stone boulders used to mark burial sites are known as:
(a) Microliths
(b) Megaliths
(c) Macroliths
(d) None of these.
Question 7. The Rigveda was written on the bark of:
(a) Palm
(b) Peepal
(c) Birch
(d) Neem
Question 8. The Rigveda was written:
(a) About 1500 yeas ago
(b) About 2000 years ago
(c) About 2500 years ago
(d) About 3500 years ago
Question 9. Where was the birch bark found on which hymns of the Rigveda were written?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Kashmir
(d) Madhya Pradesh
Question 10. Where was the first evidence of writing found around 3500 years ago?
(a) In China
(b) In Pakistan
(c) In India
(d) None of these
Question 11. Stone circles or boulders on the surface were used to cover the:
(a) All of these
(b) Burial places
(c) House
(d) Port holes
Question 12. A popular drink ______________ was prepared from milk and juice of a rare plant that grew on the mountains:
(a) Butter
(b) Soma
(c) Sura
(d) Ghee
Question 13. The Aryans had divided themselves into tribes known as:
(a) Ashtajana
(b) Panchajana
(c) Chaturthjana
(d) Saptchajana
Question 14. Sanskrit is part of a family of languages which is known as:
(a) Indo-European
(b) Indo-China
(c) Indo-Russian
(d) Indo-Dravin
Question 15. How many types of Vedas are there:
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 2
Match The Following:
Question 1. Where was the head of the dead laid at the burials found at Inamgaon?
(a) East
(b) West
(c) North
(d) South
Question 2. Vessels found at Inamgaon site, contained:
(a) Food and water
(b) Ornaments
(c) Clothes
(d) None
Question 3. The language of the Veda is:
(a) Hindi
(b) Sanskrit
(c) Vedic Sanskrit
(d) Tamil
Question 4. Which of these does not comes under the Veda?
(a) Rig
(b) Atharva
(c) Sam
(d) Puran
Question 5. Inamgaon is situated on the river Ghod which is tributary of:
(a) Bhima
(b) Ravi
(c) Vias
(d) Ganga
Question 6. Stone boulders used to mark burial sites are known as:
(a) Microliths
(b) Megaliths
(c) Macroliths
(d) None of these.
Question 7. The Rigveda was written on the bark of:
(a) Palm
(b) Peepal
(c) Birch
(d) Neem
Question 8. The Rigveda was written:
(a) About 1500 yeas ago
(b) About 2000 years ago
(c) About 2500 years ago
(d) About 3500 years ago
Question 9. Where was the birch bark found on which hymns of the Rigveda were written?
(a) Andhra Pradesh
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Kashmir
(d) Madhya Pradesh
Question 10. Where was the first evidence of writing found around 3500 years ago?
(a) In China
(b) In Pakistan
(c) In India
(d) None of these
Question 11. Stone circles or boulders on the surface were used to cover the:
(a) All of these
(b) Burial places
(c) House
(d) Port holes
Question 12. A popular drink ______________ was prepared from milk and juice of a rare plant that grew on the mountains:
(a) Butter
(b) Soma
(c) Sura
(d) Ghee
Question 13. The Aryans had divided themselves into tribes known as:
(a) Ashtajana
(b) Panchajana
(c) Chaturthjana
(d) Saptchajana
Question 14. Sanskrit is part of a family of languages which is known as:
(a) Indo-European
(b) Indo-China
(c) Indo-Russian
(d) Indo-Dravin
Question 15. How many types of Vedas are there:
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 2
Match The Following:
Fill in the blanks:
1. The Rigveda has been written in __________.
2. _________ is situated on the river Ghod.
3. The Rigveda was composed about _________ years ago.
4. _________ is part of a family of languages known as Indo-European.
5. The major gods praised in the hymns of the Rigveda were ________, _________ and ________.
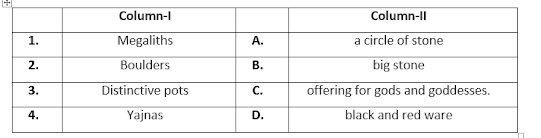
6. The dead were buried with distinctive pots, which are called _________ and _________ Ware.
Write true (T) or false (F):
1. The river Ghod is a tributary of the Bhima.
2. The oldest Veda is the Samaveda.
3. Slaves were women and men who were often captured in war.
4. Hymns were composed by sages (rishis).
5. In a hymn in the Rigveda, Vishvamitra used the word ‘sisters’ for the two rivers Beas and Sutlej.
6. Roma, a plant from which a special drink was prepared.
Very Short Questions:
1. Which is the oldest Veda among the four Vedas?
2. In which language Rigveda was written?
3. As per Rigveda, why battles were fought?
4. What are Megaliths?
5. Where was the page from a manuscript of the Rigveda found?
6. Why yajnas or sacrifices were performed?
7. Which language belongs to the Dravidian family?
8. Which language belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family?
9. Name the site where skeleton was found with 33 gold beads, 2 stone beads, 4 copper bangles, and one conch shell.
10. What is Sukta?
11. Name 4 Vedas.
12. What do people at Inamgaon ate?
13. How were yajnas performed?
14. How slaves were treated?
15. Which language belongs to the Austro- Asiatic family?
Short Questions:
1. Were some burial spots meant for certain families?
2. What were oracle bones?
3. What do circle of stone boulders or a single large stone standing on the ground indicates?
4. In what ways are the books we read today different from the Rigveda?
5. Differentiate between ‘Aryas’ and ‘Dasas’.
6. What kind of evidence from burials do archaeologists use to find out whether there were social differences amongst those who were buried?
Long Questions:
1. In what ways do you think that the life of a raja was different from that of a dasa or dasi?
2. How horses, cattle, chariot and battles are depicted in Rigveda?
3. Write a note on Rigveda.
4. Write a short note on the Wars fought in the Rigvedic period?
5. How have people in a society been depicted in the Rigveda?
6. Describe different classes or categories of people as referred or described in Rigveda.
1. The Rigveda has been written in __________.
2. _________ is situated on the river Ghod.
3. The Rigveda was composed about _________ years ago.
4. _________ is part of a family of languages known as Indo-European.
5. The major gods praised in the hymns of the Rigveda were ________, _________ and ________.
6. The dead were buried with distinctive pots, which are called _________ and _________ Ware.
Write true (T) or false (F):
1. The river Ghod is a tributary of the Bhima.
2. The oldest Veda is the Samaveda.
3. Slaves were women and men who were often captured in war.
4. Hymns were composed by sages (rishis).
5. In a hymn in the Rigveda, Vishvamitra used the word ‘sisters’ for the two rivers Beas and Sutlej.
6. Roma, a plant from which a special drink was prepared.
Very Short Questions:
1. Which is the oldest Veda among the four Vedas?
2. In which language Rigveda was written?
3. As per Rigveda, why battles were fought?
4. What are Megaliths?
5. Where was the page from a manuscript of the Rigveda found?
6. Why yajnas or sacrifices were performed?
7. Which language belongs to the Dravidian family?
8. Which language belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family?
9. Name the site where skeleton was found with 33 gold beads, 2 stone beads, 4 copper bangles, and one conch shell.
10. What is Sukta?
11. Name 4 Vedas.
12. What do people at Inamgaon ate?
13. How were yajnas performed?
14. How slaves were treated?
15. Which language belongs to the Austro- Asiatic family?
Short Questions:
1. Were some burial spots meant for certain families?
2. What were oracle bones?
3. What do circle of stone boulders or a single large stone standing on the ground indicates?
4. In what ways are the books we read today different from the Rigveda?
5. Differentiate between ‘Aryas’ and ‘Dasas’.
6. What kind of evidence from burials do archaeologists use to find out whether there were social differences amongst those who were buried?
Long Questions:
1. In what ways do you think that the life of a raja was different from that of a dasa or dasi?
2. How horses, cattle, chariot and battles are depicted in Rigveda?
3. Write a note on Rigveda.
4. Write a short note on the Wars fought in the Rigvedic period?
5. How have people in a society been depicted in the Rigveda?
6. Describe different classes or categories of people as referred or described in Rigveda.
ANSWER KEY –
Multiple Choice Answer:
1. (c) North
2. (a) Food and water
3. (c) Vedic Sanskrit
4. (d) Puran
5. (a) Bhima
6. (b) Megaliths
7. (c) Birch
8. (d) About 3500 years ago
9. (c) Kashmir
10. (a) In China
11. (b) Burial places
12. (b) Soma
13. (b) Panchajana
14. (a) Indo-European
15. (c) 4
Match The Following:
1. (c) North
2. (a) Food and water
3. (c) Vedic Sanskrit
4. (d) Puran
5. (a) Bhima
6. (b) Megaliths
7. (c) Birch
8. (d) About 3500 years ago
9. (c) Kashmir
10. (a) In China
11. (b) Burial places
12. (b) Soma
13. (b) Panchajana
14. (a) Indo-European
15. (c) 4
Match The Following:
Fill in the blanks:
1. Sanskrit
2. Inamgaon
3. 3500
4. Sanskrit
5. Agni, Indra, and Soma.
6. Black and Red
Write true (T) or false (F):
1. True
2. False
3. True
4. True
5. True
6. False
Very Short Answer:
1. The oldest Veda is the Rigveda.
2. The Rigveda is in old or Vedic Sanskrit.
3. Battles were fought for cattle, land, water and for capturing people.
4. Stone boulders used to mark burial sites are known as megaliths.
5. This manuscript of the Rigveda, on birch bark, was found in Kashmir.
6. Yajnas or sacrifices were performed to please gods and goddesses.
7. Tamil, Telugu, Kannada and Malayalam belong to the Dravidian family.
8. Language used in the north-east belongs to the Tibeto-Burman family.
9. Brahmagiri.
10. The Rigveda includes more than a thousand hymns, called sukta or “well-said”.
11. There are four of them – the Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda and Atharvaveda.
12. People at Inamgaon ate wheat, barley, rice, pulses, millets, peas and sesame.
13. Yajnas were performed by offering ghee and grains into the fire in order to please god and goddesses.
14. They were treated as the property of their owners, who could make them do whatever work they wanted
15. The languages spoken in Jharkhand and parts of central India belong to the Austro-Asiatic family.
Short Answer:
1. Sometimes, megaliths contain more than one skeleton. These indicate that people, perhaps belonging to the same family, were buried in the same place though not at the same time.
2. Around 3500 years ago, we find some of the first evidence of writing in China. These writings were on animal bones. These are called oracle bones, because they were used to predict the future.
3. Sometimes, archaeologists find a circle of stone boulders or a single large stone standing on the ground. These are the only indications that there are burials beneath.
4. The books we use are written and printed. The Rigveda was recited and heard rather than read. It was written down several centuries after it was first composed, and printed less than 200 years ago.
5.
Aryas Dasas
The people who composed the hymns described themselves as Aryas. Aryas called their opponents Dasas or Dasyus. These were people who did not perform sacrifices, and probably spoke different languages.
6. Objects were found in the grave of the dead person. Sometimes, more objects are found in one grave than in another. These finds suggest that there was some difference in status amongst the people who were buried. Some were rich, others poor, some chiefs, others followers.
Long Answer:
1. Raja Dasa or Dasi
Raja was a powerful leader who used to rule. They were often captured in war.
Raja was a free person. They were treated as the property of their owners, who could make them do whatever work they wanted.
The rajas led a luxurious life. They led a miserable life.
2. There are many prayers in the Rigveda for cattle, horses, chariot and battles. Horses were yoked to chariots that were used in battles, which were fought to capture cattle. Battles were also fought for land, which was important for pasture, and for growing hardy crops that ripened quickly, such as barley. Some battles were fought for water, and to capture people.
3. The oldest Veda is the Rigveda, composed about 3500 years ago. The Rigveda includes more than a thousand hymns, called sukta or “well-said”. These hymns are in praise of various gods and goddesses. Three gods are especially important: Agni, the god of fire; Indra, a warrior god; and Soma, a plant from which a special drink was prepared. These hymns were composed by sages (rishis). Most of the hymns were composed, taught and learnt by men. A few were composed by women. The Rigveda is in old or Vedic Sanskrit.
4. Battles were fought for cattle, land, water, and to capture people. Some of the wealth that was obtained was kept by the leaders, some was given to the priests and the rest was distributed amongst the people. Some wealth was used for the performance of yajnas or sacrifices in which offerings were made into the fire. These were meant for gods and goddesses. Most men took part in these wars. There was no regular army, but there were assemblies where people met and discussed matters of war and peace. They also chose leaders, who were often brave and skilful warriors.
5. According to the Rigveda, there are two groups of people in terms of their work:
(i) The priests, called Brahmins, and (ii) The 'rajas.
The priests performed various rituals while the 'rajas' ruled. These rajas' did not, however, have capital cities, palaces or armies, nor did they collect taxes. Two words were used to refer to the people or the community as a whole those words were 'jana' and Vish'.
The people who composed the hymns referred to themselves using the word 'Aryas' and called their opponents 'Dasas' or 'Dasyus, The 'dasas' were later slaves and were treated as the property of their owners.
6. Words of the Rigveda to describe different classes or categories of the people:
• There are several ways of describing people—in the terms of the work they do, the language they speak, the place they belong to, their family, their communities and cultural practices.
• Broadly speaking, we can confess that there are two groups (of people) who are described in terms of their work—the priests, sometimes called brahmins, who performed various rituals for the rajas. These rajas were not like the ones you will be learning about later (in coming chapters). They did not have capital cities or armies, nor did they collect taxes. Generally, sons did not succeed fathers automatically.
• Two words were used (in the Rigveda) to describe people or the community as a whole. One was the word jana, which we still use in Hindi and other languages. The other was Vish. The word Vaishya comes from Vish.



























0 Comments